The Entrepreneurial Operating System (EOS) framework
- Yasir Ali Warraich

- Jul 7, 2025
- 9 min read
“Why do some businesses thrive with clarity and momentum, while others stay stuck in chaos?”
If you’re a founder, team leader, or someone trying to bring order to fast-growing business operations, chances are you’ve struggled with structure. Projects pile up, meetings go nowhere, and accountability disappears. That’s where a system like EOS (Entrepreneurial Operating System) can truly change how your business runs.
In this article, we’ll explore the EOS framework in detail, show how it connects to business automation and transformation, and demonstrate how tools like ClickUp can help make EOS work for you better than other platforms.
What Is the Entrepreneurial Operating System or EOS?
EOS is a simple yet powerful framework designed to help entrepreneurs and leadership teams get better at three things:
Vision: Getting everyone on the same page
Traction: Instilling focus and discipline
Healthy: Building a strong, functional leadership team
Created by Gino Wickman, EOS is not a software or app. It’s a business operating framework with core tools to manage and grow your organization efficiently.
Key Components of the Entrepreneurial Operating System (EOS)
The six key components of the Entrepreneurial Operating System (EOS), a comprehensive framework designed to help businesses achieve clarity, focus, and growth. These components – Vision, People, Data, Issues, Process, and Traction – work together to create a cohesive and effective management system.
By mastering these elements, organizations can streamline operations, improve communication, and ultimately achieve their strategic goals.

1. Vision: Getting Everyone on the Same Page
Vision is the cornerstone of EOS. It's about defining where the company is going and how it's going to get there. A clear and well-articulated vision ensures that everyone in the organization is aligned and working towards the same goals.
This component focuses on answering eight key questions:
What are your core values? These are the guiding principles that define the company's culture and how it operates. They should be authentic and consistently upheld.
What is your core focus? This is the company's niche or unique selling proposition. It's what the company is passionate about and where it excels.
What is your 10-year target? This is a long-term, aspirational goal that provides a clear direction for the company's future.
What is your marketing strategy? This outlines the target market, the message, and the methods used to reach customers.
What is your 3-year picture? This is a more concrete vision of what the company will look like in three years, including key milestones and achievements.
What is your 1-year plan? This breaks down the 3-year picture into specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals for the current year.
What are your quarterly rocks? These are the most important priorities for the next 90 days, designed to move the company closer to its 1-year plan.
What are your issues? Identifying and addressing the obstacles that are preventing the company from achieving its vision.

By answering these questions and regularly revisiting them, companies can create a shared understanding of their vision and ensure that everyone is working towards the same objectives.
2. People: Ensuring You Have the Right People in the Right Seats
Having the right people in the right seats is crucial for success. This component focuses on assessing and managing employees to ensure they are a good fit for their roles and the company culture.
EOS uses two key tools to evaluate people:
The People Analyzer: This tool helps determine if an employee aligns with the company's core values. Employees are rated as either "yes," "no," or "maybe" for each core value. If an employee consistently receives "no" ratings, it may be a sign that they are not a good fit for the company.
The Accountability Chart: This chart visually represents the company's structure and the roles and responsibilities of each position. It helps ensure that everyone understands their accountabilities and who they report to. Each role should have a clear set of responsibilities, and the person in that role should be capable of fulfilling those responsibilities.
The goal is to have employees who "Get it, Want it, and have the Capacity to do it" (GWC). "Get it" means they understand the role and the company's vision. "Want it" means they are passionate about the role and motivated to succeed. "Capacity" means they have the skills and abilities to perform the role effectively.
3. Data: Measuring Progress and Making Informed Decisions
Data provides objective information that helps companies track progress, identify problems, and make informed decisions.
This component focuses on establishing a set of key performance indicators (KPIs) that are regularly monitored and reviewed.
Scorecard: A weekly scorecard tracks critical numbers for the company and each department. These numbers should be leading indicators that provide early warning signs of potential problems. The scorecard should be reviewed weekly by the leadership team to identify trends and take corrective action when necessary.
Measurables: Each employee should have at least one measurable that tracks their performance. These measurables should be aligned with the company's overall goals and provide employees with clear targets to strive for.
By tracking and analyzing data, companies can gain valuable insights into their performance and make more informed decisions. This helps to identify areas for improvement and ensure that the company is on track to achieve its goals.
4. Issues: Identifying, Discussing, and Solving Problems
Every company faces issues, but the key is to have a structured process for identifying, discussing, and solving them.
This component focuses on creating a culture of open communication and problem-solving.
IDS (Identify, Discuss, Solve): This is a simple but effective process for addressing issues. First, the issue is clearly identified. Then, it is discussed openly and honestly. Finally, a solution is developed and implemented.
Issue List: Maintaining a running list of issues that need to be addressed. This list should be reviewed regularly by the leadership team to prioritize and address the most important issues.
The goal is to create a culture where issues are seen as opportunities for improvement, rather than problems to be avoided. By addressing issues proactively and systematically, companies can prevent them from escalating and hindering their progress.
5. Process: Documenting and Following Core Processes
Consistent processes ensure that tasks are performed efficiently and effectively.
This component focuses on documenting and following the company's core processes.
Documenting Core Processes: Identifying and documenting the 20% of processes that drive 80% of the results. These processes should be clearly defined and documented so that everyone in the company understands how they work.
Following Core Processes: Ensuring that everyone in the company follows the documented processes. This requires training, communication, and accountability.
By standardizing core processes, companies can improve efficiency, reduce errors, and ensure consistency in their operations. This also makes it easier to train new employees and scale the business.
6. Traction: Instilling Discipline and Accountability
Traction is about instilling discipline and accountability throughout the organization.
This component focuses on setting clear goals, tracking progress, and holding people accountable for their results.
Rocks: Setting quarterly rocks, which are the most important priorities for the next 90 days. These rocks should be aligned with the company's 1-year plan and contribute to its overall vision.
Meeting Pulse: Implementing a regular meeting schedule to track progress, address issues, and ensure accountability. This typically includes weekly leadership team meetings, monthly departmental meetings, and quarterly planning sessions.
Accountability: Holding people accountable for their rocks and measurables. This requires clear expectations, regular feedback, and consequences for not meeting expectations.

By instilling discipline and accountability, companies can ensure that everyone is focused on achieving the company's goals and that progress is being made consistently.
The Benefits and Drawbacks of EOS
Benefits
Clear direction and focus
Improved team alignment
Regular problem-solving and tracking
Structured meetings and measurable outcomes
Scalable processes and systems
Drawbacks
Not plug-and-play: requires effort to implement
Some teams resist structure or discipline
Time investment to see results

Cons of an EOS Framework and Ways to Mitigate Them
Rigid structure → Flex tools like ClickUp to make EOS flexible and visual.
Requires full buy-in → Start with one department or team before scaling.
Difficult tracking manually → Use automation tools like ClickUp to track Rocks, To-Dos, and Scorecards.

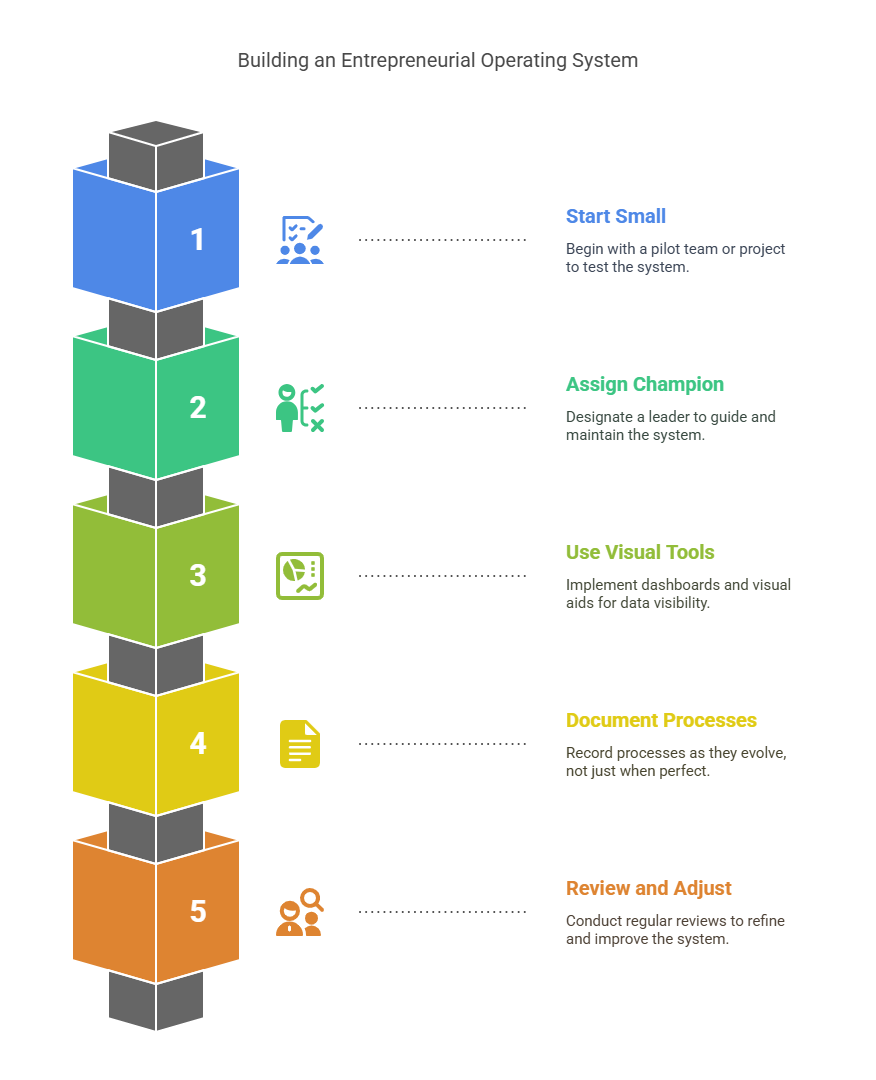
Tips for Building an Entrepreneurial Operating System
Start small: Pilot EOS with one team or project.
Assign an EOS Champion to keep things on track.
Use visual tools and dashboards to keep data visible.
Document as you go—don’t wait for perfect processes.
Review every 90 days and adjust.
Power Up Your EOS Implementation With ClickUp
ClickUp is more than just a task manager—it’s a full platform that mirrors the EOS structure:

Vision and Goals: Use Docs and Dashboards for your Vision/Traction Organizer.

People and Roles: Assign responsibilities using ClickUp’s customizable Workspace Hierarchy.

Scorecards and Measurables: Build weekly dashboards that automatically update your KPIs.

Issues and IDS: Track issues and problem-solving with task lists and comments.

Meetings and Rocks: Plan Level 10 meetings, assign Rocks, and track progress in real time.

Process Documentation: Use Docs, Checklists, and Automations to standardize operations.
ClickUp lets you automate, collaborate, and scale—without overwhelming your team. It combines clarity with flexibility, giving EOS a digital life.
Similar Tools and How They Compare With ClickUp
While there are many project management tools on the market, ClickUp remains the preferred choice for EOS users.
ClickUp Comparison with other similar tools:
Asana is clean but lacks deep customization and advanced dashboards.
Jira is ideal for dev teams but too technical for general business use.
Monday looks good visually, but may require more effort to build out EOS-like structures.
Trello is great for light tasking but not for serious scaling or reporting.
Notion allows documentation but lacks integrated task-tracking and automation at scale.
Smartsheet offers spreadsheets with logic, but it’s not ideal for team collaboration.
Airtable mixes databases with workflows but needs external add-ons for full EOS support.
Wrike has strong project tools, but it can feel complex for small teams.

ClickUp, by contrast, covers task management, knowledge base, automation, reporting, and collaboration—all in one tool. It aligns naturally with EOS.
How EOS Improves Business Automation and Team Focus
Automation isn’t just about swapping human effort with software—it’s about freeing your team to focus on the work that matters most. EOS brings laser‑sharp clarity to what needs automating by grounding every task in measurable business goals (your “Measurables” and “Rocks”).
Once you identify repetitive, low‑value tasks, you can:
Document the Process using the EOS 3‑Step Process Documenter.
Automate the Workflow with ClickUp’s no‑code Automations and Integrations.
Monitor Results on an EOS‑style Scorecard in real time.
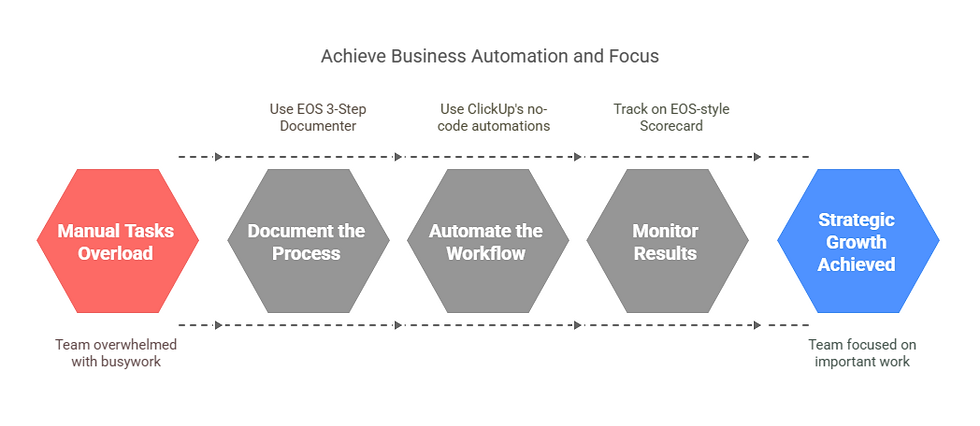
The result? A team that spends less time on busywork and more time driving strategic growth, because everyone can see exactly how their work supports the vision.
Why Structure Drives Growth (and What EOS Teaches Us)
Many founders feel that structure will slow them down. In reality, structure is the skeleton that lets you sprint without tripping.
EOS teaches that growth hinges on:
Clear Roles: The Accountability Chart eliminates overlapping responsibilities.
Consistent Processes: Documented workflows slash onboarding time and errors.
Regular Cadence: Level 10 Meetings and quarterly planning create a rhythm of execution.

By standardizing the how, EOS liberates the what: innovation, customer delight, and new‑market expansion. Teams move faster because decisions flow through defined channels instead of bottlenecks.
Common Mistakes While Implementing EOS and How to Fix Them
When implementing EOS, many teams fall into avoidable traps that slow down progress. One of the most common mistakes is skipping vision work—teams end up pulling in different directions. A focused Vision/Traction Organizer (V/TO) session and documenting your vision clearly in ClickUp Docs can resolve this.
Another issue is setting too many Rocks, which leads to burnout and scattered focus. Limit your Rocks to 3–5 each quarter and track them visually on a ClickUp Dashboard.
Teams also tend to treat Scorecards as "nice-to-have" tools. This can lead to decisions based on intuition rather than data. The fix? Embed your Scorecards in every team’s ClickUp homepage to keep metrics top of mind. Similarly, ignoring process documentation leads to confusion and inconsistency. Use ClickUp Docs to standardize workflows and attach Loom walkthroughs where needed.
Lastly, neglecting people's issues may erode your culture over time. The People Analyzer can be reviewed quarterly to surface performance or values alignment gaps—address them promptly through regular IDS sessions. With the right awareness and tools like ClickUp, these common missteps can be avoided or corrected early.

Common FAQs
Q: Do I need a coach to implement EOS? A: Not necessarily, but having a facilitator or an EOS-trained consultant can speed up your success.
Q: Can small teams use EOS? A: Yes, EOS is scalable. Small teams benefit by bringing clarity and alignment from the start.
Q: Is ClickUp officially an EOS software? A: No, but it's one of the most EOS-compatible tools available.
Q: How long does it take to see results? A: With consistent effort, most teams see measurable progress in 3–6 months.
Q: Can I run EOS and other frameworks together? A: Yes, but it’s best to focus fully on EOS if you’re just starting.
Conclusion
The Entrepreneurial Operating System (EOS) offers a clear, proven way to bring structure, accountability, and direction to your organization. But frameworks alone aren’t enough—implementation is everything. This is where the power of the right tools comes into play. Platforms like ClickUp make it easier to apply EOS principles in your daily operations, from managing Rocks to solving Issues and running effective meetings.
While other platforms offer similar functionality, ClickUp brings it all together under one roof, helping your team stay aligned, productive, and laser-focused. By combining the clarity of EOS with the flexibility and automation of ClickUp, you’re setting your team up for measurable growth and long-term success.
Need expert help implementing this? Click here to start with a free consultation.



Comments