Critical Chain Project Management (CCPM): How to Manage Constraints"
- Yasir Ali Warraich

- Aug 26, 2025
- 7 min read
Every project manager has faced this moment: the deadline is coming closer, resources are stretched thin, and the team feels the pressure of limited time, people, or budget. No matter how carefully you plan, constraints are always there—they can delay progress, affect costs, or push teams to compromise on quality.
This is where Critical Chain Project Management (CCPM) becomes a game-changer. Unlike traditional methods that focus mostly on tasks and schedules, CCPM zooms in on constraints—the real bottlenecks that can slow down the entire project.
And here’s where today’s world takes this method to another level: Artificial Intelligence (AI). With the rise of AI-powered project management tools, constraints don’t have to be invisible anymore. AI can detect them early, predict delays, and suggest better workflows to keep projects on track.
Among the tools available, ClickUp stands out as a leading solution that blends CCPM with AI-driven features—making it easier than ever to manage projects under pressure.
Understanding Critical Chain Project Management (CCPM)
CCPM is a project management method developed by Dr. Eliyahu M. Goldratt in the 1990s. Instead of focusing only on the critical path (the longest sequence of dependent tasks), CCPM shifts attention to the critical chain—which includes not just task dependencies but also resource constraints.
In simpler words:
Traditional methods → focus on task order.
CCPM → focus on both task order and limited resources.
The goal? To finish projects faster and with less stress by protecting the schedule from delays.
Why CCPM Matters Today
Modern projects are more complex, involving remote teams, digital tools, and tight budgets. That means constraints multiply—not just time, but also:
Limited skilled people
Software dependencies
Hardware shortages
Client approvals
Market shifts
AI tools now integrate with CCPM to help managers see these constraints early, analyze their impact, and suggest practical ways to manage them.
The Problems with Traditional Project Management
Traditional project management methods, like CPM, often suffer from several drawbacks:
Student Syndrome: Team members tend to delay starting tasks until the last possible moment, assuming they have ample time.
Parkinson's Law: Work expands to fill the time available for its completion, leading to inefficiency.
Multitasking: Resources are often assigned to multiple tasks simultaneously, resulting in delays and reduced quality.
Lack of Buffer Management: Traditional methods often lack effective mechanisms for managing project buffers, making projects vulnerable to delays.

The CCPM Solution: Focus on Constraints
CCPM addresses these issues by focusing on identifying and managing the project's constraints. The constraint is the resource or activity that limits the project's ability to achieve its goals. By focusing on the constraint, CCPM aims to optimize the entire project flow.
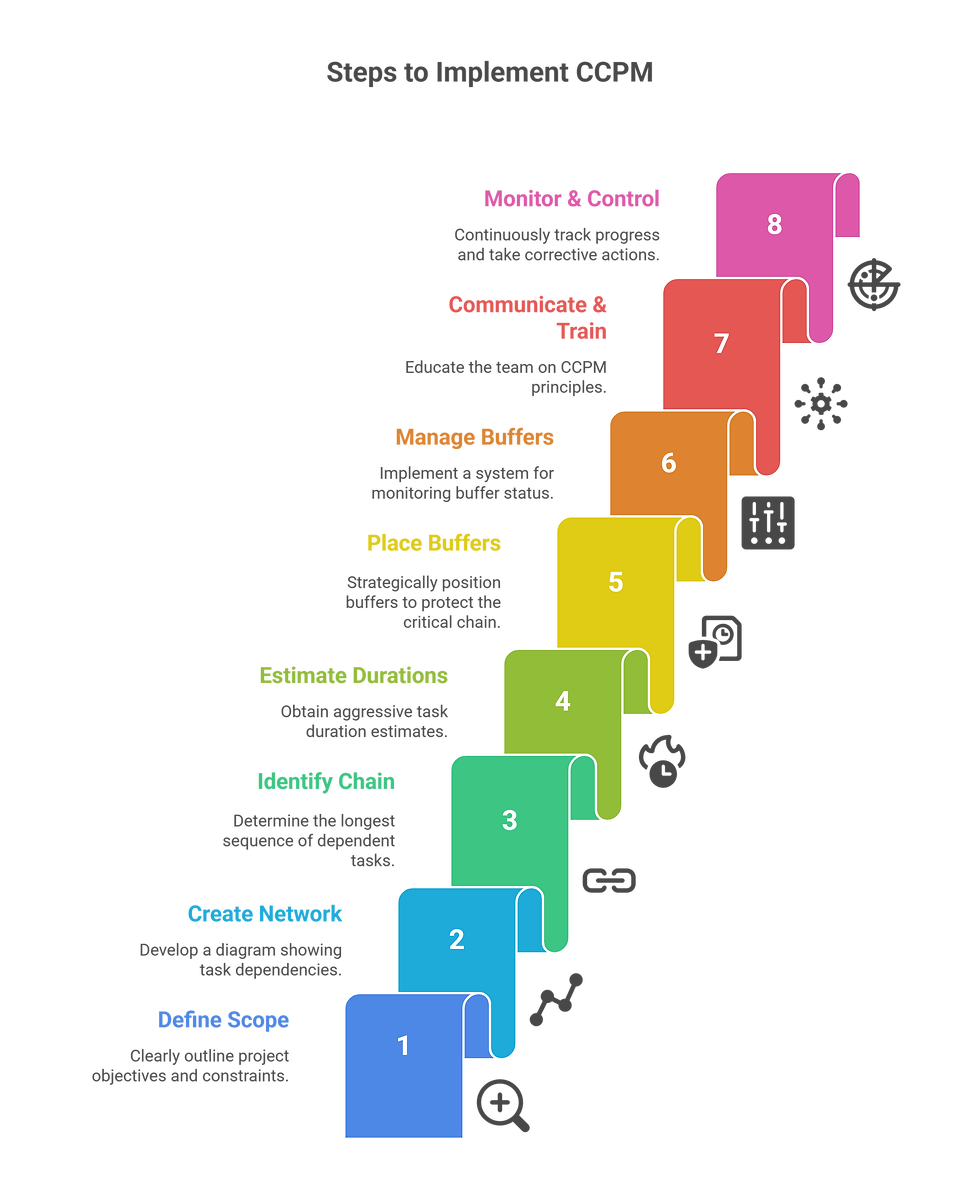
Implementing CCPM: A Step-by-Step Guide
Implementing CCPM involves several steps:
Define the Project Scope: Clearly define the project's objectives, deliverables, and constraints.
Create a Project Network Diagram: Develop a network diagram that shows the dependencies between tasks.
Identify the Critical Chain: Determine the longest sequence of dependent tasks, considering both task dependencies and resource constraints.
Estimate Task Durations: Obtain aggressive task duration estimates from project team members.
Place Buffers: Strategically place project, feeding, and resource buffers to protect the critical chain.
Develop a Buffer Management System: Implement a system for monitoring the status of the buffers and triggering corrective actions when necessary.
Communicate and Train: Communicate the principles of CCPM to the project team and provide training on how to implement the methodology.
Monitor and Control: Continuously monitor the project's progress and take corrective actions as needed to keep the project on track.
Core Principles of CCPM
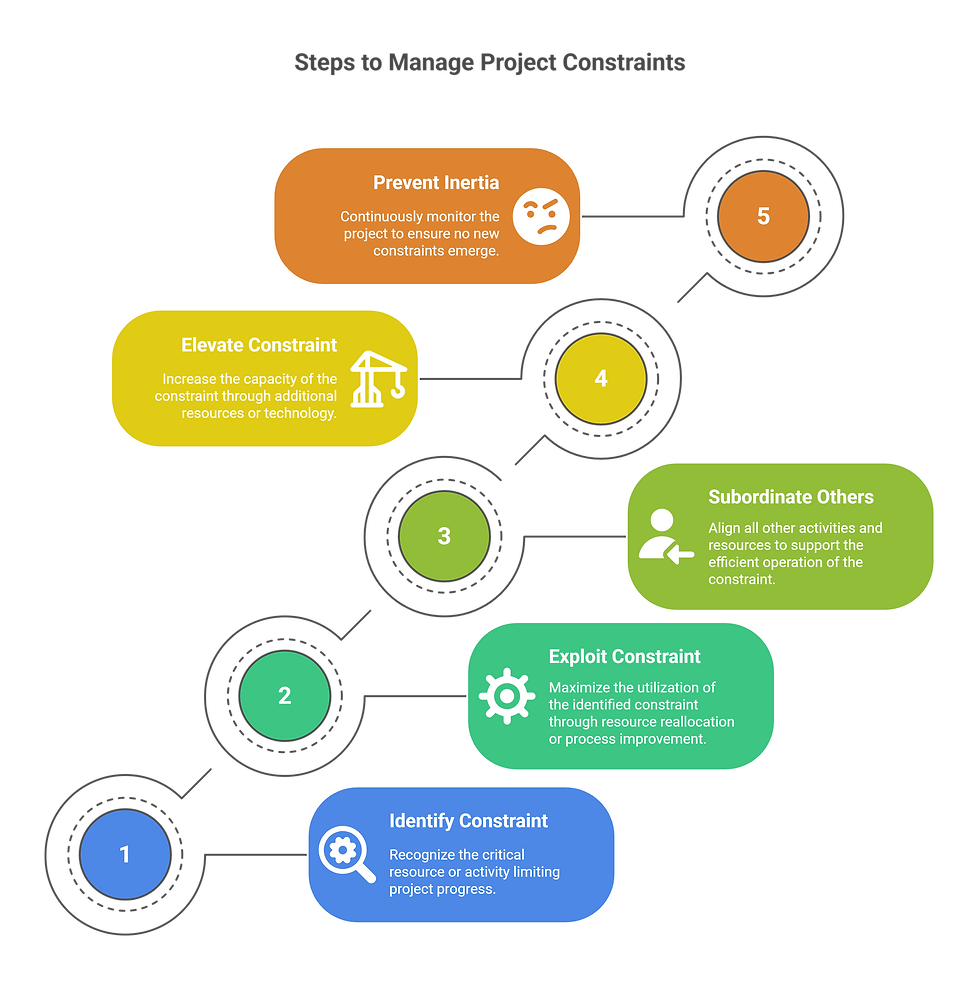
CCPM is based on several core principles:
Identify the Constraint: The first step is to identify the project's constraint, which is typically a resource or a critical path activity.
Exploit the Constraint: Once the constraint is identified, the next step is to exploit it, meaning to maximize its utilization. This may involve reallocating resources, streamlining processes, or improving communication.
Subordinate Everything Else: All other activities and resources should be subordinated to the constraint, meaning they should be aligned to support the constraint's efficient operation.
Elevate the Constraint: If the constraint is still limiting the project's performance, the next step is to elevate it, meaning to increase its capacity. This may involve adding more resources, investing in new technology, or outsourcing tasks.
Don't Allow Inertia to Cause a Constraint: Once the constraint is resolved, it's important to continuously monitor the project to ensure that a new constraint doesn't emerge.
Key Tools and Techniques in CCPM
CCPM employs several key tools and techniques to manage projects effectively:

1. Critical Chain Scheduling
Critical Chain Scheduling is the core of CCPM. It involves creating a project schedule that considers both task dependencies and resource constraints.
Task Duration Estimates: Unlike traditional methods, CCPM uses aggressive task duration estimates, typically around 50% of the traditional estimates. This encourages team members to focus on completing tasks efficiently.
Resource Allocation: Resources are allocated to tasks based on their availability and skills, ensuring that critical resources are not over-allocated.
Buffer Insertion: Buffers are inserted into the schedule to protect the project from delays caused by task variability.
2. Project Buffer
A Project Buffer is a time buffer inserted at the end of the critical chain to protect the project's completion date from delays. It absorbs the variability in task durations and prevents delays from cascading through the project.
3. Feeding Buffers
Feeding Buffers are time buffers inserted at the end of non-critical chains before they merge into the critical chain. They protect the critical chain from delays in non-critical tasks.
4. Resource Buffers
Resource Buffers are alerts placed before critical chain tasks that require specific resources. These alerts ensure that the necessary resources are available when needed, preventing delays caused by resource unavailability.
5. Drum-Buffer-Rope (DBR)
Drum-Buffer-Rope (DBR) is a production scheduling method used to manage the flow of work through the project.
Drum: The drum represents the project's constraint, which sets the pace for the entire project.
Buffer: The buffer protects the drum from disruptions, ensuring that it always has work to do.
Rope: The rope is a communication mechanism that ensures that work is released into the project at the same rate as the drum's capacity.
6. Buffer Management
Buffer Management is the process of monitoring the status of the project buffers and taking corrective action when necessary. It involves tracking buffer consumption and identifying the root causes of delays.
Buffer Status Monitoring: Regularly monitor the status of the project, feeding, and resource buffers to identify potential delays.
Root Cause Analysis: When a buffer is consumed, investigate the root cause of the delay to prevent similar issues from occurring in the future.
Corrective Action: Take corrective action to address the root causes of delays and prevent further buffer consumption.
AI in CCPM: Enhancing Project Management
Artificial Intelligence (AI) can significantly enhance CCPM by automating tasks, improving decision-making, and providing valuable insights.

1. AI-Powered Task Duration Estimation
AI algorithms can analyze historical project data to predict task durations more accurately than traditional methods. This can help to create more realistic project schedules and reduce the need for excessive buffers.
2. AI-Driven Resource Allocation
AI can optimize resource allocation by considering factors such as resource availability, skills, and task dependencies. This can help to ensure that critical resources are allocated to the most important tasks and that resources are not over-allocated.
3. AI-Based Buffer Management
AI can monitor buffer consumption in real-time and identify potential delays before they impact the project. It can also analyze the root causes of delays and recommend corrective actions.
4. Predictive Risk Management
AI algorithms can analyze project data to identify potential risks and predict their impact on the project. This can help project managers to proactively mitigate risks and prevent delays.
5. Automated Reporting and Analytics
AI can automate the generation of project reports and provide valuable insights into project performance. This can help project managers to track progress, identify trends, and make data-driven decisions.
ClickUp: A Powerful Tool for CCPM Implementation
ClickUp is a versatile project management platform that can be used to implement CCPM effectively. Its flexible features and customizable interface make it an ideal choice for managing projects of all sizes and complexities.

How ClickUp Supports CCPM
Customizable Task Management: ClickUp allows you to create custom task statuses, priorities, and tags to track the progress of tasks and identify potential delays.

Resource Management: ClickUp's resource management features allow you to allocate resources to tasks, track resource availability, and identify resource bottlenecks.
Gantt Charts: ClickUp's Gantt charts provide a visual representation of the project schedule, making it easy to identify the critical chain and track buffer consumption.

Automation: ClickUp's automation features allow you to automate repetitive tasks, such as sending notifications, updating task statuses, and creating reports.

Integrations: ClickUp integrates with a wide range of other tools, such as Slack, Google Calendar, and Microsoft Teams, making it easy to collaborate with team members and stakeholders.

ClickUp and AI
ClickUp is continuously integrating AI-powered features to enhance project management capabilities. While specific AI features for CCPM are evolving, ClickUp's AI can assist with:
Smart Task Suggestions: AI can suggest relevant tasks based on your current workload and project priorities.
Automated Summaries: AI can generate summaries of project progress and highlight key issues.
Predictive Risk Analysis: AI can analyze project data to identify potential risks and recommend mitigation strategies.

Comparison with Other Tools
While other tools provide useful features, here’s how ClickUp holds an advantage:
Ease of Use – Many tools feel too rigid or too complex. ClickUp offers a clean interface with customizable views that make CCPM practical.
AI Integration – Few tools have built-in AI writing, task prioritization, and predictive analytics at the same level.
Flexibility – Unlike platforms that lock you into one method, ClickUp allows you to mix CCPM with Agile, Scrum, or Kanban.
Cost-Effectiveness – ClickUp combines features from multiple apps into one, saving both money and effort.
Collaboration – Team chat, docs, dashboards, and whiteboards all live in the same space—keeping CCPM communication transparent.

While other options exist, ClickUp consistently comes out stronger when managing constraints with CCPM + AI.
Here's the full ClickUp comparison with other tools.
Practical Tips for Managing Constraints with CCPM
Always define your critical chain before you start.
Use AI dashboards to monitor workload in real time.
Protect your timeline with properly sized buffers.
Review resource allocation weekly to avoid hidden bottlenecks.
Automate repetitive updates—freeing time for problem-solving.

The Future of CCPM with AI
In the future, AI will not just assist but lead CCPM strategies by:
Running “what-if” simulations instantly.
Suggesting alternative schedules when constraints shift.
Learning from past projects to improve accuracy.
Acting as a project co-pilot—answering questions in natural language.

Imagine asking your AI assistant in ClickUp: “Where’s my biggest risk this week?” and instantly getting a visual answer. That’s the future of CCPM—and it’s already starting to happen.
Conclusion
Critical Chain Project Management is all about managing constraints. In today’s complex business environment, AI takes CCPM to the next level by predicting risks, optimizing resources, and automating routine work.
While many tools support CCPM, ClickUp stands out as the #1 choice because of its AI features, flexibility, and focus on real-time constraint management.
If you’re serious about managing projects effectively—where deadlines are real, resources are limited, and success depends on speed—then CCPM with ClickUp is the smart move forward.
Inspired by this solution? Let’s tailor it for your business – schedule your free strategy session now.



Comments